QUANTICA Occitania
Quantifying the additional soil carbon stock allowed by intermediate cover in agriculture
Project completedThrough extensive coordination, the Quantica project has laid the technological groundwork for measuring carbon sequestration at the plot level using cover crops. The tools for visualizing the results and all of the project's resources are available on a single website.
This remote sensing-based approach is recommended by the Bas Carbone label for more accurate estimation of the impact of cover crops on soil carbon storage.
OVERVIEW
Carbon storage in soils is a lever for achieving the objective of reducing net greenhouse gas emissions. Depending on the nature and occupation of the land, new agricultural practices can increase these stocks, which is known as the additional storage potential. According to INRAE studies, "intermediate" crops represent 35% of the total additional storage potential in France.
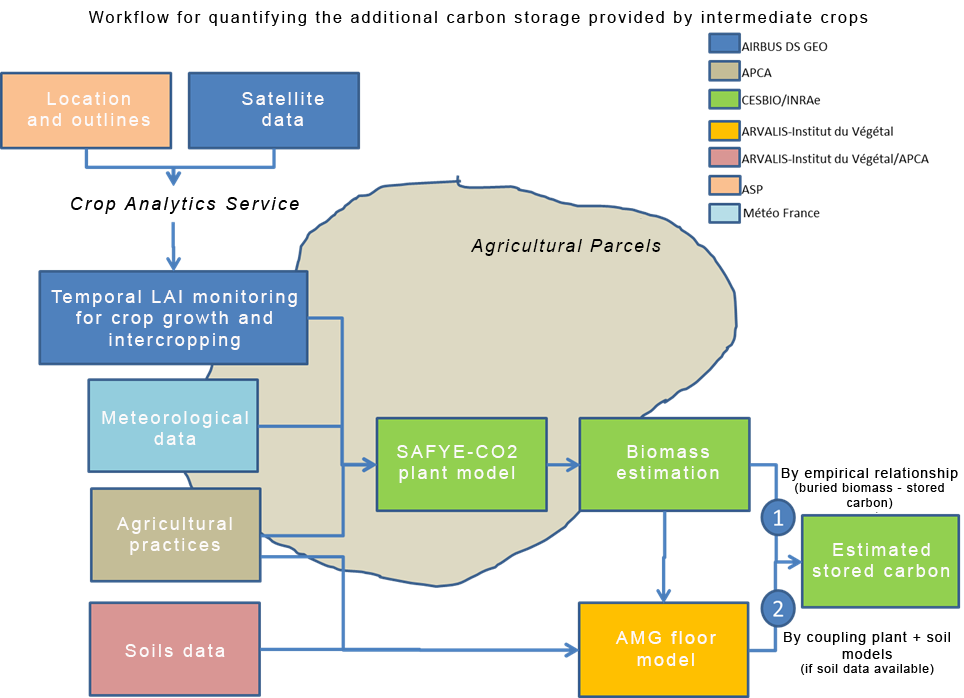
The quantification of additional carbon storage in agricultural soils is based can be supported by a method developed at CESBIO combining satellite observation technologies for crops and intermediate crops and agro-environmental modeling (SAFYE-CO2 model included in the AgriCarbon-EO operational processing chain and calibrated from high resolution time series derived from satellite images). Through this process, the model is forced to reproduce the dynamics and development intensity (biomass) of intermediate crops. It also simulates the components of the carbon balance (photosynthesis, plant and soil respiration). Coupling SAFYE-CO2 with the AMG soil model can enable a more accurate calculation of the additional carbon storage induced by intermediate crops thanks to a more precise estimate of the biomass returned to the soil. The coupling of these models then provides an evaluation tool compatible with the Low Carbon Label methodology.
The development of the tool and the prototyping of future operational services were based on user-centered approaches, Living Lab approach, by iterative cycles of specification / development / delivery.
With the ambition to improve the technological maturity level of the QUANTICA software and to make the design of the service chain evolve, the living lab approach relied on an interface prototyping tool that contributes to the design of 3 complementary services:
- Collection of information provided by farmers (via API MesP@arcelles of APCA),
- Readability and cross-referencing of the indicator at the right scale and relationship with other necessary data (or interoperability),
- Significant interfaces for farmers in a context of valorisation of the practice: low carbon label, CAP, carbon offset market.
Application site(s)
The Occitanie region, and more specifically the departments of Gers and Tarn, with the support of the agro-ecology and digital Living Lab "OCCITANUM", including the open lab "field crops".
DATA
Satellite
- Time series of biophysical variables (e.g. leaf area index or LAI) from Sentinel-2 - Landsat8 - SPOT6/7 archive images provided by the Crop Analytics tool for the detection of the presence of intermediate crops and the quantification of their development level. The Crop Analytics tool, developed by AIRBUS DS, will automatically monitor in real time the dynamics of LAI evolution estimated by satellite. Crop Analytics automatically performs the following operations: collection of available free satellite images (e.g. Sentinel-2), cleaning of these images (clouds, etc.), calculation of biophysical variables and delivery of these variables to the plots of interest on the basis of their geolocated crop contours.
Others
- Data on agricultural parcels from the national Graphical Parcel Register for the purposes of modeling crop growth and identifying intercrop periods. These data, in particular the contours of agricultural parcels and the succession of crops per parcel, are provided by the Agence des Services et Paiement (ASP) and IGN.
- Data related to agricultural practices for the purpose of modeling additional carbon stored in the soil. Type of intermediate crop and date of destruction, type and quantity of carbon exported at harvest in the form of grain, straw, etc., type and quantity of organic amendments, this information is collected via the farm information systems, in this case MesP@rcelles of the National Network of Chambers of Agriculture (APCA).
- Spatialized meteorological observations, for example from the SAFRAN database of Météo-France, for crop growth modeling purposes.
- Data on the physico-chemical properties of the soils on the plots studied for the purposes of modeling the dynamics of organic carbon in soils (input data for the AMG model), provided by ARVALIS-Institut du Végétaland/or by the farmers themselves.
RESULTS - FINAL PRODUCTS
The Quantica project has enabled testing of the SAFYE-CO2 plant model coupled with the AMG soil model on new cover crops implemented by polycultivators and livestock farmers belonging to the GIEE (Economic and Environmental Interest Group) of the Association for the Creation of the Astarac Regional Nature Park.
All the resources used and a tool for viewing the results are available on a free website, and these elements will evolve over time.
|
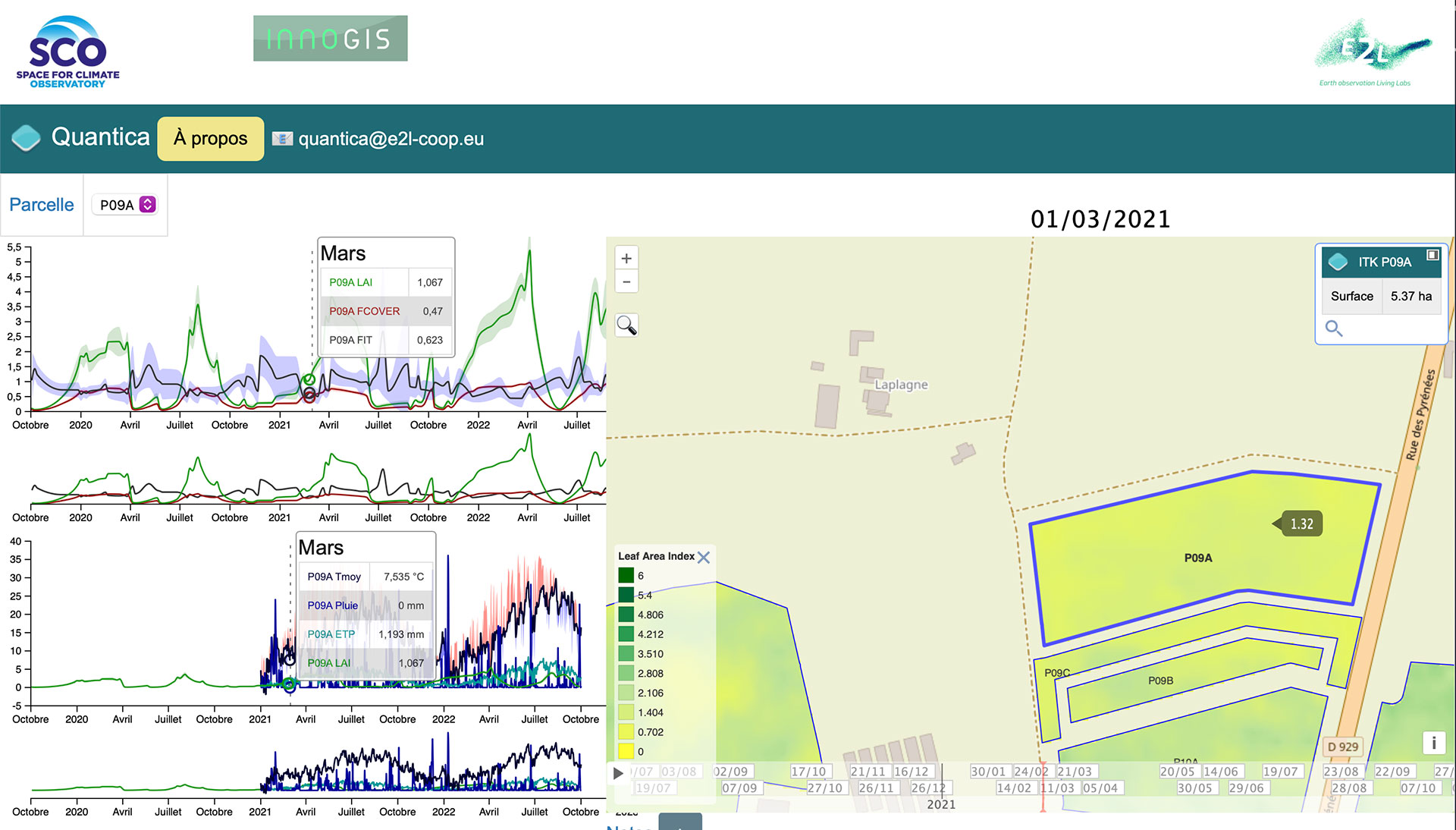
◀︎ Quantica visualization interface. The results come from processing information provided by farmers (intermediate farming practices), cross-referenced with spatial data (Sentinel 2 satellites) and model results, at the plot level. |
|
The Quantica project has thus demonstrated the value of remote sensing coupled with modeling (SAFYE-CO2) for estimating the biomass of intermediate cover crops as accurately as possible, which is then used as input data for the AMG soil model. In particular, it revealed a significant underestimation of carbon storage on certain plots when using generic values defined by the Carbon Agri or Grandes Cultures methods.
With satisfactory results despite significant heterogeneity in biomass within plots, the spatial block provided by Quantica can therefore be used in a Low Carbon Label approach. This type of approach based on remote sensing is even recommended by the LBC and avoids reductions in the credits received by farmers.
Project news
- 21/12/2023: Presentation of the QUANTICA project and its progress at the 11th SCO France Quarterly Meeting "Innovative services for resilient farming practices".
Newsletter QUANTICA (in French)
- Newsletter n°3 - 09/06/2023
- Newsletter n°2 - 22/02/2023
- Newsletter n°1 - 22/11/2022