FY-PM
Estimation of PM2.5 and PM10 in China
Overview
This study proposes to use a machine learning model to directly populate the missing TOAR (Top-of-the-Atmosphere Reflectance) data, thereby generating a fully-covered TOAR dataset under hypothetical clear-sky conditions. This dataset is then combined with meteorological factors for estimating particulate matter concentrations, effectively improving the temporal resolution and spatial coverage of the particulate matter data.
In this study, the field-observed PM10 and PM2.5 data, TOAR data, meteorological factors, and geographic information were integrated to achieve high temporal and spatial resolution and full coverage of Chinese particulate matter data using machine learning models. And the model performance results of particulate matter estimation under multiple scenarios are explored.
|
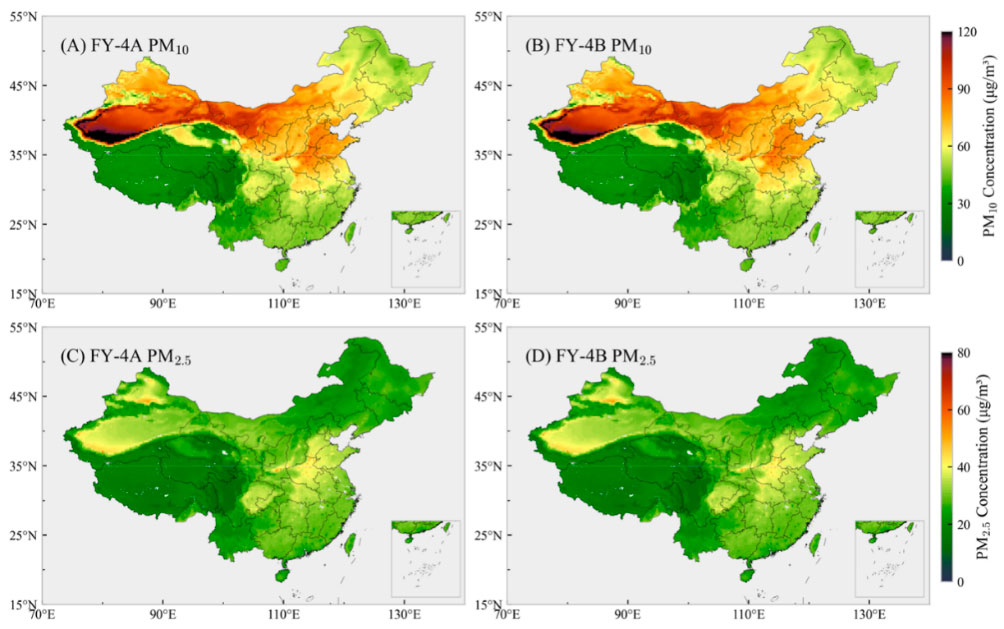
◀︎ Annual average distribution of PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations in 2022-2023. The left and right columns show the results of FY-4A and FY-4B, respectively, proving no significant differences between the two sets of findings of these two distinct meteorological satellites. © Lanzhou University |
Application site(s)
Beijing, China
Data
Satellite
- TOAR data from Fengyun FY-4A and FY-4B satellites, which includes four bands: 0.45–0.49 μm (blue band), 0.55–0.75 μm (green band), 0.75–0.90 μm (red band), and 2.1–2.35 μm (near-infrared band).
- Cloud detection product (CLM) for cloud removal processing, with a spatial resolution of 4 km.
Other
- Meteorological Parameters from the ERA5 reanalysis of the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF): boundary layer height, 2 m temperature, relative humidity, and 10 m wind components, as well as surface pressure. The above data are.
- Geographical Information Data:
- low and high vegetation indices (ECMWF ERA5);
- elevation data from the SRTM-3 dataset with a spatial resolution of 90 m (NASA and the National Imagery and Mapping Agency NIMA);
- population density data with a spatial resolution of 0.04° × 0.04° (2015 UN-adjusted population data provided by NASA's Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center SEDAC).
- Particle concentration data from the China National Environmental Monitoring Center.
Results - Final product(s)
The main output of this project includes a high spatiotemporal resolution dataset of atmospheric particulate matter concentrations. By utilizing the synergistic observation data from the Fengyun-4A and Fengyun-4B satellites and the extreme tree model, the project will generate fully covered TOAR filling data under assumed clear sky conditions and estimate particulate matter concentrations based on this data.
These output data can be used for air quality monitoring and research, significantly enhancing the coverage and accuracy of existing data.
End users include researchers and students. Data will be presented in map format. Data can be obtained from the project manager using the contact form below.